1. What is the current carrying capacity of 32amp rated cable, if it is protected by the rewireable fuse?
A 13 Amp
B 16 Amp
C 26 Amp
D 39 Amp
2. What is the possible range to measure the size of the wire in a Standard Wire Gauge (SWG)?
A 0-44
B 0-42
C 0-38
D 0-36
3. What is the name of the wire joint?

B Knotted tap joint
C Duplex cross tap joint
D Double cross tap joint
4. Which type of soldering flux is used for soldering galvanised iron?
A Rosin
B Zinc chloride
C Sal ammonia
D Hydrochloric acid
5. Which method of soldering is used for quantity production and for tinning work?
A Dip soldering
B Soldering with a flame
C Soldering with soldering iron
D Soldering with soldering gun
6. What is the name of the part marked as X in the underground (UG) cable?

B Armouring
C Lead sheath
D Paper insulation
7. What is the full form of XLPE Cable?
A Cross Line Poly Ethylene
B X’ess Line Phase Earthing
C Cross Linked Poly Ethylene
D Excess Length Paper and Ebonite
8. What is the purpose of ‘serving’ layer in underground cable?
A Protect the cable from moisture
B Protect the cable from mechanical injury
C Protect metallic sheath against corrosion
D Protect armouring from atmospheric condition
9. Which type of fault of U.G Cable can be located by this loop test?

B Short circuit fault
C Open circuit fault
D Weak insulation fault
10. Which cable laying method is used in generating station?
A In ducts
B Racks in air
C Along buildings
D Direct in ground
11. How many electrons are there in the valence shell of a copper atom?
A 1
B 2
C 8
D 18
12. What is the effect of electric current on neon lamp?
A Heating effect
B Magnetic effect
C Chemical effect
D Gas ionization effect
13. What is the unit of insulation resistance?
A Ohm
B Kilo ohm
C Milli ohm
D Mega ohm
14. Which electrical device is the coarse excess current protection?
A Cartridge fuses
B Rewirable fuses
C Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
D High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) Fuses
15. Which type of joint is used for extending the length of conductor in over head lines?
A Scarfed joint
B Aerial tap joint
C Britannia T joint
D Western Union joint
16. Which type of soldering flux is used for soldering aluminium conductors?
A Tallow
B Ker-al-lite
C Zinc chloride
D Sal ammonia rosin
17. What is the effect on molten solder due to repeated melting?
A Tin content reduced
B Lead content reduced
C Prevent slug formation
D Uneven flowing in joints
18. What will happen to PVC insulation in cable carries excess current continuously for long period?
A Voltage drop increases
B Voltage drop decreases
C Insulation resistance increases
D Insulation resistance decreases
19. Which method of cable laying is suitable for congested areas?
A Racks in air
B Duct pipes
C Along buildings
D Direct in ground
20. What is the name of the part marked X in UG cables?

B Bedding
C Armouring
D Lead sheath
21. What is the fault of U.G cable identified in the circuit?
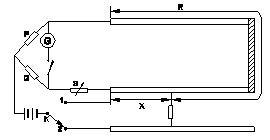
B Short circuit fault
C Open circuit fault
D Weak insulation fault
22. Which part of the underground cable is protecting the metallic sheath against corrosion?
A Serving
B Bedding
C Armouring
D Lead sheath
23. Why the soldering iron must be kept into a stand that not in use while soldering?
A It prevents burns and fire
B To control the excessive heat
C To save the time of soldering process
D To save the operator from electric shock
24. Which type of wire joint is found in the junction box?
A Aerial tap joint
B Plain tap joint
C Rat tail joint
D Married joint
25. What is the name of the joint?

B Scarfed joint
C Western union joint
D Britannia straight joint
26. What is the use of Britannia T joint?
A Extending the length of the lines
B Inside and outside wiring installation
C Mechanical stress not required on conductor
D Tapping the service connection from overhead lines
27. Which type of soldering method is used for servicing and repairing work?
A Dip soldering
B Soldering with a flame
C Soldering with soldering gun
D Soldering with a soldering iron
28. What is the use of dip soldering method?
A Soft soldering
B Piping and cable soldering work
C Soldering miniature components on PCB
D Soldering sensitive electric components
29. Name the part marked X of belted U.G cable.

B Armouring
C Lead sheath
D Paper insulation
30. Which insulating material is used as hot pouring compound for making joints in underground cable?
A Polyamine hardener
B Cast resin compound
C Bituminous compound
D Epoxy cast resin compound
31. What is the purpose of bedding insulation of U.G. cable?
A Protect the cable from mechanical injury
B Protect the cable from moisture and gases
C Protect armouring from atmospheric condition
D Protect the metallic sheath against corrosion
32. Which test is conducted to locate the faults in U.G. cables?
A Loop test
B External growler test
C Break down voltage test
D Insulation resistance test
33. What does the number 1.40 represent if a stranded conductor is designated as 7/1.40?
A Area of cross section
B Radius of one conductor
C Diameter of all conductor
D Diameter of each conductor
34. What is the value of electrical conductivity of aluminium conductor?
A 61 mho/m
B 56 mho/m
C 35 mho/m
D 28 mho/m
35. What is the rating factor of cable provided with coarse excess current protection?
A 1.11
B 1.23
C 0.81
D 0.707
36. What is the size of neutral conductor compared to phase conductor in U.G cable?
A Same size of phase conductor
B Half size of phase conductor
C 1/4 size of phase conductor
D 1/3 size of phase conductor
37. What is the name of the tool?

B Wire stripper
C Crimping tool
D Side cutting plier
38. What is the reading of the micrometer?
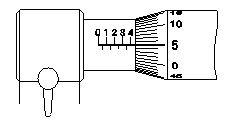
B 5.00 mm
C 4.55 mm
D 4.05 mm
39. Which method of soldering is used for repairing the vehicle body?
A Dip soldering
B Soldering with flame
C Soldering with soldering iron
D Soldering with soldering gun
40. What is the advantage of stranded conductor over solid conductor?
A Cost is less
B More flexible
C Less voltage drop
D More insulation resistance
41. What is the current capacity of the 16 Amp. Cable, if it is protected by coarse excess current protection?
A 11 A
B 13 A
C 15 A
D 18 A
42. What is the unit for Quantity of electricity?
A Mho
B Coulomb
C Volt /second
D Ampere/second
43. What is the name of the soldering method?

B Soldering iron
C Soldering gun
D Soldering with flame
44. What formula is used to find Electro Motive Force (EMF)?
A EMF = Potential difference – voltage drop
B EMF = Potential difference + voltage drop
C EMF = Potential difference + voltage drop/2
D EMF = Potential difference + 2 x voltage drop
45. What is the current rating factor for close excess current protection of cable?
A 0.81
B 0.92
C 1.23
D 1.5
46. What is the disadvantage of solid conductor compared to stranded conductor?
A Less rigidity
B Less flexibility
C Low melting point
D Low mechanical strength
47. What is the name of the soldering method?
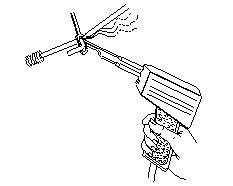
B Soldering with blow lamp
C Soldering with soldering gun
D Temperature controlled soldering
48. What is the cause for cold solder defect in soldering?
A Excessive heating
B Insufficient heating
C Incorrect use of solder
D High wattage soldering iron
49. What happens to the voltmeter if it is connected as an ammeter?
A Low reading
B No deflection
C Meter burns out
D Overshoot deflection
50. Which is the example for coarse excess current protection?
A MCB
B MCCB
C H.R.C fuses
D Rewireable type fuse unit
51. Which conductors are used for distribution lines?
A Insulated conductors
B Insulated solid conductors
C Bare conductors
D Two core cable



0 Comments